
20 February, 2025
Understanding the Lifespan of USB Drives
USB Drives offer a practical and efficient way to carry and share data. For businesses, custom-printed promotional USB drives are an excellent medium for promotional activities, often branded and distributed as part of marketing strategies. However, an often-overlooked aspect in promotional planning is understanding their lifespan. There are factors that influence their longevity.
Understanding USB Drive Technology
USB drives are based on flash memory technology, a type of non-volatile storage that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. Unlike traditional hard drives, they have no moving parts, making them more durable and resistant to mechanical failures. The core component is the NAND flash memory chip, which dictates its storage capacity and speed.
NAND Flash Memory: At the core of every USB drive is the NAND flash memory chip. This type of memory is known for its high storage density and compact size. NAND flash memory stores data in an array of memory cells made from floating-gate transistors. These cells retain data even without power, making USB drives an excellent medium for long-term data storage.
Data Storage Mechanism: Data is stored in the form of electrical charges in these cells. The presence or absence of charge in each cell represents binary data (bits). This method of data storage, unlike the magnetic method used in traditional hard drives, contributes to the drive's durability and shock resistance.
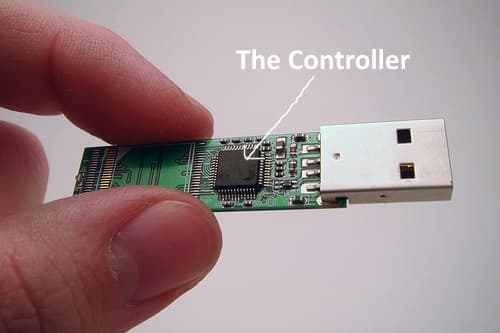
The Controller: Brain of the USB Drive
Role of the Controller: A crucial but often overlooked component is its controller. This microcontroller manages the data storage process, including error correction, wear levelling, and interfacing with the host device. It plays a pivotal role in determining the speed and efficiency of data transfer.
Error Correction Code (ECC): The controller uses ECC to detect and correct common types of data corruption. This feature is vital for maintaining data integrity, especially as the drive ages.
Speed and Performance
Read/Write Speeds: The performance is largely dependent on its read and write speeds. These speeds are influenced by the quality of the NAND flash memory and the efficiency of the controller. Higher-end USB drives offer faster data transfer rates, which is crucial for transferring large files or frequent data access.
USB Standards: The speed is also impacted by the USB standard with which the drive is compatible. For example, USB 3.0 and 3.1 drives offer significantly faster transfer rates than their USB 2.0 counterparts.
Durability and Reliability
No Moving Parts: The absence of moving parts in them provides a distinct advantage over traditional hard drives. This not only makes them less susceptible to mechanical failures but also more suitable for use in mobile and harsh environments.
Wear Levelling: To prolong the life of the drive, most incorporate wear levelling algorithms. This technique ensures the erasing and rewriting processes are distributed evenly across the memory cells, preventing premature wear in specific areas.
Temperature Resistance: They are generally resistant to extreme temperatures, which adds to their robustness and reliability in varied environmental conditions.
Capacity and Form Factor
Evolving Storage Capacities: Over the years, the storage capacity has increased dramatically, with options now ranging from a few gigabytes to several terabytes, accommodating different user needs.
Compact and Customisable Design: The small form factor makes them extremely portable. Additionally, they offer ample opportunities for customisation, making them popular as promotional items or personal accessories.

Lifespan Factors
The lifespan of a USB drive is determined by several key factors:
1. Write and Erase Cycles
Nature of the Cycles: Each time a file is saved or deleted, the flash memory cells undergo a 'write' or 'erase' cycle. These cycles involve applying electrical charges to the memory cells, which gradually degrades their ability to hold these charges reliably.
Finite Lifespan: Flash memory cells can only withstand a limited number of write and erase cycles. Once this limit is reached, the cells may fail to store data correctly. The typical range for these cycles can vary significantly based on the quality of the flash memory. Lower-end drives might offer thousands of cycles, whereas high-end models can endure hundreds of thousands.
Impact on Longevity: The rate at which these cycles are used up directly influences the lifespan of the USB drive. Ones used for frequent, intensive read/write operations will reach their cycle limit sooner than those used more sparingly.
2. Quality of Components
Memory Chip Quality: The grade of the NAND flash memory chip is crucial. Grade A chips have lower failure rates and a higher tolerance for write/erase cycles compared to lower-grade counterparts.
Controller Quality: The microcontroller, which manages data storage and retrieval, also impacts longevity. High-quality controllers are more efficient in managing tasks like wear levelling and error correction, thereby extending the drive's usable life.
Overall Build Quality: The physical construction of it, including its casing and connector, also plays a role. Drives with robust and durable builds are more likely to withstand physical wear and tear over time.
3. Usage Patterns
Intensity and Frequency of Use: Ones that are frequently written to and erased or used for running live operating systems will wear out faster than those used less often or primarily for read-only data storage.
Data Management Practices: Proper data management, such as safely ejecting the drive and avoiding unnecessary write operations, can prolong its life.
4. Environmental Conditions
Temperature Extremes: They are sensitive to extreme temperatures. Prolonged exposure to high heat can damage the electronic components, while extreme cold can make materials brittle and more prone to physical damage.
Moisture and Humidity: Exposure to moisture can lead to corrosion of electronic circuits and connectors.
Magnetic Interference: Strong magnetic fields can potentially corrupt data stored on it, although this is less of a concern for flash memory compared to magnetic storage media.
5. Storage Capacity Utilisation
Impact of Full Capacity Use: Continually operating at near its maximum capacity can strain the flash memory cells. It limits the effectiveness of wear levelling algorithms, as there are fewer free cells to distribute write and erase cycles evenly.
Optimal Capacity Management: To maximise lifespan, it's advisable to use only a portion of the drive's total capacity for regular storage, leaving some space free to aid in wear levelling and to ensure optimal performance.
The longevity is shaped by a confluence of factors, including the quality of its components, how it's used, the conditions it's exposed to, and how its storage capacity is managed. Understanding and mitigating these factors can significantly enhance the lifespan and reliability of these indispensable data storage devices.
Average Lifespan Expectations
The average lifespan of a USB drive is a topic of considerable interest, especially considering their widespread use in various applications, from personal data storage to business and promotional uses. While giving a precise lifespan is difficult due to numerous influencing factors, a general expectation can be outlined.
General Lifespan Range
Typical Duration: Under normal usage conditions, a standard one can last anywhere from 5 to 10 years. This estimation is based on the average quality and usage patterns of typical consumer-grade ones.
Longevity Factors: The lifespan is significantly influenced by the frequency and intensity of use, the quality of the components, environmental conditions, and how well the drive's capacity is managed as outlined previously.
Influence of Quality and Usage
High-Quality Drives: Ones with high-grade memory chips and robust controllers are likely to last on the longer end of the spectrum, potentially even exceeding 10 years. These drives are better equipped to handle a large number of write/erase cycles and are less prone to errors and data corruption.
Usage Intensity: Ones that are frequently written to and erased or used for tasks such as running operating systems or continuous data logging may experience a shorter lifespan. Intensive use accelerates the wear on the flash memory cells, hastening their decline.
Understanding Normal Conditions
Defining 'Normal' Use: Normal conditions typically involve moderate use, where it is used for storing and transferring files intermittently, rather than constant read/write operations. This includes using it for file backups, occasional media storage, or light office work.
Environmental Impact: Normal conditions also assume a relatively stable and benign environment, free from extreme temperatures, high humidity, or exposure to harsh conditions that could physically damage it or its electronic components.
Predicting and Extending Lifespan
Monitoring for Signs of Wear: Users can sometimes notice signs of wear, such as slower performance, difficulty in file transfers, or errors during use. These signs can indicate it is approaching the end of its useful life.
Extending Lifespan: To maximise its lifespan, it is recommended to use it within its capacity limits, avoid exposing it to extreme conditions, and ensure that it is disconnected or powered down when not in use.
The average lifespan of a USB drive is influenced by a combination of factors including quality, usage patterns, and environmental conditions. While a general range of 5 to 10 years can be expected, this can vary widely based on individual circumstances. Understanding and managing these factors can help in optimising the lifespan of these versatile storage devices.
Implications for Promotional Planning
When incorporating USB drives into promotional strategies, businesses should consider the following to maximise their effectiveness.
1. Quality Selection
Long-Term Brand Association: Opting for higher quality ones is crucial for sustaining a positive brand image. A drive that lasts longer and performs reliably will keep the brand in good standing with the recipients for an extended period.
Cost vs. Quality Balance: While high-quality ones may incur a higher upfront cost, they offer better value in the long run through sustained brand exposure and reduced replacement costs.
2. Capacity Choice
Matching Capacity to Use-Case: Selecting the right storage capacity is essential. For most promotional uses, moderate capacities (like 8GB to 16GB) are sufficient for recipients to store and transfer documents and media.
Cost-Effectiveness: Larger capacities might seem appealing but can unnecessarily increase costs. It's important to balance the utility with budget considerations.
3. Data Preloading
Immediate Value Addition: Preloading them with promotional materials, such as catalogues, product videos, or software demos, can offer immediate value to the recipient and serve as a direct marketing tool.
Consideration of Usability: While preloading uses some of its write cycles, the impact is usually minimal compared to the drive's total lifecycle. However, ensure the preloaded content does not consume too much of the drive’s available space, preserving its utility for personal use.
4. Customisation and Branding
Reflecting Brand Identity: Customised designs and branding on them should be thoughtfully designed to reflect the brand's identity and message.
Durability of Customisation: Ensure the branding, whether it's printed, engraved, or embossed, is durable and doesn't wear off easily, as this can impact the perceived quality of the brand.
5. Educating Recipients
Providing Care Instructions: Including tips on proper usage and care can enhance their longevity. Simple advice on avoiding exposure to extreme conditions, safely ejecting the drive, and avoiding overfilling the storage can be very helpful.
Enhancing User Experience: Educating recipients not only helps in extending the lifespan, but also demonstrates the brand's commitment to providing value beyond just the physical product.
The Final Byte
Understanding their lifespan is crucial in promotional planning. By selecting quality drives, considering usage patterns, and staying informed about tech trends, businesses can maximise their promotional impact. When used wisely they can be a potent tool in a marketing arsenal, offering a tangible brand experience in our increasingly digital world.
The Custom USB Drives Team




